Latest Posts
Which SD Card Capacity Do You Need? SD vs SDHC vs SDXC vs SDUC Guide
Choosing the right SD card can feel overwhelming with options like SD, SDHC, SDXC, and SDUC. However, selecting the correct capacity is essential. A card too small can force you to constantly delete files, while one too large may leave you paying for unused space. This guide breaks down SD card types to help you find the best fit for your needs, whether for photos, videos, or apps.
Understanding the Four Types of SD Cards
SD cards come in four types, each designed for specific storage capacities and file systems. Here’s an overview:
SD Standard (Up to 2GB)
- Capacity: Up to 2GB
- File System: FAT12 and FAT16
These original SD cards are versatile and compatible with all devices supporting SD, SDHC, SDXC, and SDUC. They’re ideal for small files but limited by today’s standards.
SDHC Cards (2GB-32GB)
- Capacity: 2GB to 32GB
- File System: FAT32
Introduced after 2008, SDHC cards work with SDHC, SDXC, and SDUC devices. They’re perfect for general use like photography and basic storage.
SDXC Cards (32GB-2TB)
- Capacity: 32GB to 2TB
- File System: exFAT
Released in 2009, SDXC cards are excellent for storing high-resolution images and videos. They’re supported by SDXC and SDUC devices.
SDUC Cards (2TB-128TB)
- Capacity: 2TB to 128TB
- File System: exFAT
The newest addition, SDUC cards, offers massive storage capacities for advanced use cases. They require SDUC-compatible devices.
|
Card Type |
Capacity Range |
File System |
|
SD |
Up to 2GB |
FAT12/16 |
|
SDHC |
2GB-32GB |
FAT32 |
|
SDXC |
32GB-2TB |
exFAT |
|
SDUC |
2TB-128TB |
exFAT |
Choosing the Right SD Card Capacity
The right SD card depends on your storage needs and intended use. Let’s explore key considerations:
Storage Requirements by Use Case
- Photography and General Use: 64GB to 256GB cards are usually sufficient.
- 4K Video Recording: Opt for SDXC cards with larger capacities to handle high-bitrate footage.
- Gaming or App Storage: Consider capacities above 128GB to accommodate large file sizes.
Cost per Gigabyte
Price often depends on capacity, but larger cards typically offer better value per gigabyte. Look for cards with TLC NAND Flash technology for cost-efficiency without compromising performance.
Future-Proofing
Storage demands are growing. Many modern games and apps now require over 100GB. To future-proof:
- Ensure your device supports newer SD card standards.
- Factor in the growing file sizes of media and applications.
- Choose a card with room to grow beyond your current needs.
SD Card Speed Classes and Performance
Speed class ratings measure a card’s minimum write speed. This is critical for activities like video recording or file transfers.

Speed Class Ratings
These are the most basic performance indicators:
- Class 2: 2MB/s
- Class 4: 4MB/s
- Class 6: 6MB/s
- Class 10: 10MB/s
UHS Speed Classes
Ultra High Speed (UHS) cards offer better performance:
- U1: 10MB/s minimum write speed.
- U3: 30MB/s minimum write speed.
UHS cards use specific bus interfaces:
- UHS-I: Max speeds of 104MB/s.
- UHS-II: Max speeds of 312MB/s.
- UHS-III: Max speeds of 624MB/s
Video Speed Class
For advanced video recording, Video Speed Classes are critical:
- V6: 6MB/s
- V10: 10MB/s
- V30: 30MB/s (suitable for 4K recording)
- V60: 60MB/s
- V90: 90MB/s (needed for 8K video)
Manufacturers often exceed these baseline speeds, ensuring reliable performance.
Common SD Card Compatibility Issues
SD card issues often arise due to compatibility problems. Here’s how to avoid them:
Device Compatibility Matrix
- SDUC cards: Only work with SDUC devices.
- SDXC cards: Compatible with SDXC and SDUC devices.
- SDHC cards: Work with SDHC, SDXC, and SDUC devices.
- Standard SD cards: Universal compatibility with all devices.
Operating System Support
- exFAT: Supported natively on Windows Vista SP1 and later, macOS 10.6.5 and newer.
- FAT32: Widely supported but limited to 4GB file sizes.
Older systems may require patches or firmware updates for compatibility.
Format and File System Limitations
- FAT32 is ideal for broad compatibility but unsuitable for large files.
- exFAT removes size restrictions but isn’t supported by older devices.
Use the official SD Card Formatter tool to ensure proper formatting and troubleshoot issues like improper card seating or device firmware limitations.
Future of SD Card Technology
SD card technology continues to advance, promising exciting possibilities:
- SD Express: Combines PCIe and NVMe architectures for transfer speeds up to 2GB/s.
- Self-Encrypted Drives: Enhance security with built-in encryption.
- Thermal Management: Improves performance and durability.
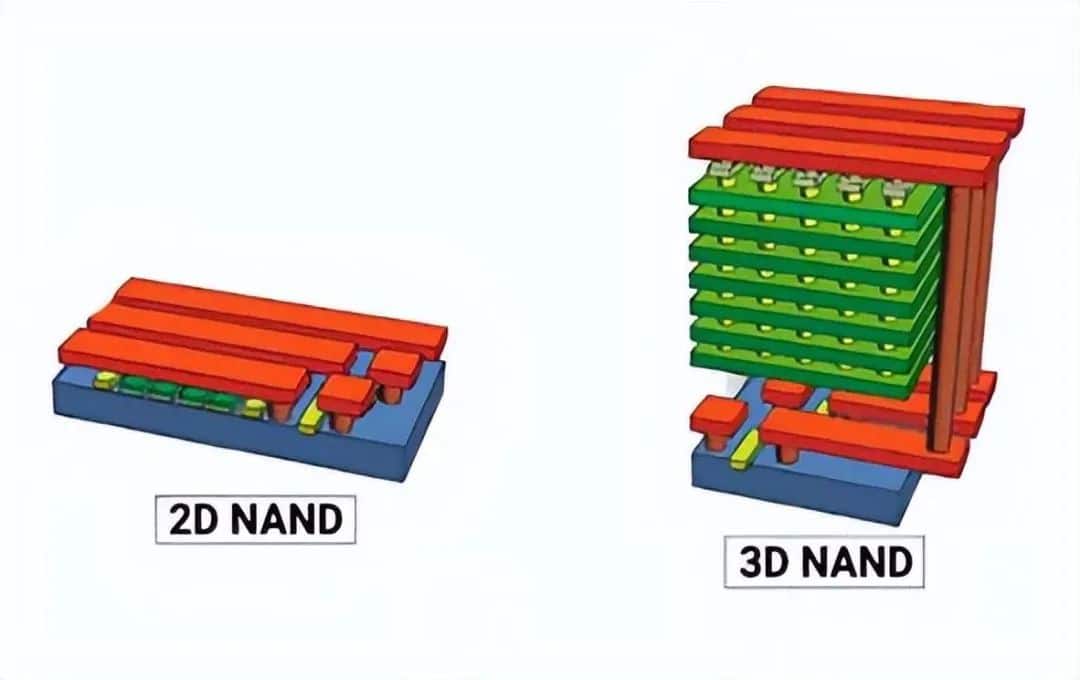
- 3D NAND Technology: Stacks memory cells vertically, increasing storage density and reducing costs.

Western Digital’s 8TB SD card is a game-changer, and SD 9.1 specifications introduce new speed classes ranging from 150 to 600. These innovations support demanding tasks like AI processing, high-resolution video capture, and edge computing.
Conclusion
SD cards have evolved to meet diverse storage needs, from standard 2GB cards to SDUC formats capable of holding up to 128TB. Selecting the right card requires careful consideration of storage capacity, speed class ratings, and device compatibility.To make the best choice:
- Match the card type to your device’s specifications.
- Plan for both current and future storage demands.
- Verify speed class requirements for your intended use.
- Check operating system compatibility and file system limitations.
By understanding these factors, you can choose an SD card that fits your needs perfectly and delivers reliable performance.









Leave a comment