Latest Posts
what is Data storage?
- Definition of data storage
- Text File for the Data Storage System: Microsoft Excel, Microsoft Access and Visual FoxPro
- Data storage methods: DAS, NAS, SAN
- Development of data storage
- Market demand
- Cloud storage
Definition of data storage
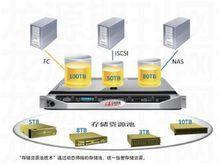
Storage resource pool
In a broad sense, data storage is information organization. It is a manifestation of well-organized information and its use at various times.
Data storage is an information organization process in and of itself, and it is a forward-thinking one. It is, however, not the same as simple information arrangement. It considers aspects such as the efficient utilization of channel capacity and the access efficiency of stored data. In a broad sense, it is the extension of information organization during the information transmission process.
Depending on the application context, data storage is a service in which operators or service providers store data on specified media in an acceptable, safe, and effective manner and can ensure effective access.
Data storage system
Text file

A text file is the most ubiquitous data storage tool and comes with every computer. However, it is rarely utilized to store a huge amount of data in actual system applications, and it is primarily used to retain minimal information or setup values. When the amount of information is huge, the readability of the information is substantially diminished, and the data’s security and integrity cannot be properly assured because of its basic format and simple editor. This format is commonly used in the system to record data that has fewer information and no format constraints, making it easier to read and alter for users.
Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a vital component of Microsoft’s office suite. It is commonly used for data statistics, analysis, and processing, among other things. Many individuals use it to store data because of how simple it is to use. Excel stores data in cells, which are the smallest storage units. Its worksheet is made up of rows of Arabic numerals and columns of English letters, with the rows and columns intersecting to make many cells.
Microsoft Access
Microsoft Access is a crucial component of Microsoft’s office suite. Microsoft released a desktop relational database management system (RDBMS) for Windows. Tables, queries, forms, reports, pages, macros, and modules are among the objects that can be used to create a database system. It also includes a number of wizards, generators, and templates that may be used to develop a set of standardized data storage, query, interface design, and report creation activities. Users can quickly set up a full-featured database management system. They may also execute most data management jobs without having to write a lot of codes throughout the use process since they are freed from tiresome coding tasks.
Visual FoxPro
Visual FoxPro, abbreviated as VFP, is a database development software created by Microsoft. To create a database, it is simple and convenient to use. Visual FoxPro 9.0 is the most recent version. However, the classic version of Visual FoxPro 6.0 is still utilized in school instruction and education agency examinations. Its processing speed is among the fastest among desktop database apps, and it is a great helper in daily tasks.
Data storage methods
DAS
Direct Attached Storage (DAS), which is to connect the device directly to the bus, is the same as the storage architecture of a common PC. This storage method determines that the 1 0 read and write and storage management need to be completed by the server host, and all data maintenance and management operations need to occupy server resources. This kind of resource occupation is especially obvious in data backup operations, which can consume 20 percent to 30 percent of server resources. As a result, backup operations for this storage architecture are typically performed late at night, rather than during working hours, to prevent disrupting normal operations. The larger the amount of data in direct-attached storage, the longer the backup and recovery time, and the greater the dependence and impact on server hardware.
NAS
A storage tool
The previously inefficient DAS storage technology has been vastly improved by Network Attached Storage (NAS). It switches the storage’s role from being tied to the server to being an independent network node in the network, allowing users to access the storage directly. The independent storage server also ensures access efficiency and frees up resources on the application server, as the storage does not take up any of the application server’s resources.
SAN
The storage network is created using the SAN (Storage Area Network) approach. SAN is clearly following the historical trend in the Internet era. Fibre Channel (FC) technology is the SAN’s supporting technology. It is a standard integration for network and channel I/O interfaces that ANSI has defined. HIPPI, IPI, SCSI, IP, and ATM are just a few of the high-level protocols supported by FC technology. Its most important characteristic is that it separates the network and equipment’s communication protocols from the transmission physical medium, allowing various protocols to be sent over the same physical link at the same time.
Even when large amounts of data are stored, the fibre link connecting the SAN network storage device and the server can ensure that the device consumes nearly little LAN traffic. This high-speed communication route between the server and the SAN storage device also allows the server to access any storage device at any time, ensuring data availability. In applications that require high performance and reliability, the SAN data storage network provides data storage, backup, and other operations without occupying the bandwidth of the LAN, lowering network load, and ensuring the normal and smooth operation of the applications in the network. At the same time, the fibre channel’s high-speed data transfer rate eliminates the need for tasks like data backup to take too long.
Development of data storage
Data storage and storage management technology originated from the terminal-host computing model in the 1970s. Data was concentrated on the host at the time, and hard disks and disks attached to the host served as the primary storage and backup devices.
Data storage became spread after the 1980s, thanks to the rise of personal computers and, in particular, the creation of the client/server architecture. Important data is often focused on the network’s file server and database server at this time, and there is also a certain amount of data on the client computer. Data dissemination makes data storage management more difficult.
In the 1990s, the rapid development of the Internet transformed storage technologies. This shift may be seen in three ways: the first is the rapid expansion of storage capacity, which increases the need for storage servers. The second factor is the lengthening of data. Network data is now available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, thanks to the Internet. Finally, the management of data storage is subjected to more stringent criteria. Data diversification, geographical dispersion, and the safeguarding of sensitive data have all raised the stakes for data management. In response to these shifts, networked storage, such as NAS and SAN, arose, separating storage devices from application servers for centralized management.
Market demand
With the start of the new century, the rate of development of data information and e-commerce has accelerated even more, and business information systems have steadily taken over as the primary source of competitive advantage. Businesses rely on data more than ever before. And with stricter data readiness requirements, today’s network data must be available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year.
Data access should be controlled by security methods rather than geographical area limits in today’s Internet and worldwide e-commerce era. The data recorded by the computer is directly tied to the profit, survival, and growth of the business, especially in industries like finance and telecommunications. As a result, in enterprise application systems, data security and data storage and backup are becoming increasingly important.
It’s fair to say that the demand for data storage and backup among businesses has never been higher than it is now. According to IDC’s figures and estimates, storage demand accounted for 50% of total IT demand in 2001. Storage product sales in China were 3.5 billion yuan in 2002, and are expected to reach 30.5 billion yuan in 2003. According to a Gartner/Dataquest poll conducted in the United States, the SSP (Storage Service Provider) industry is expected to reach $8 billion in 2003.
It’s fair to say that the demand for data storage and backup among businesses has been growing continually. According to data published by IDC, storage demand accounted for 50% of total IT demand in 2001. The Chinese market for storage devices reached 3.5 billion yuan in the same year, and 30.5 billion yuan in 2003. According to a Gartner/Dataquest survey conducted in the United States, the SSP (Storage Service Provider) industry was worth $8 billion in 2003.
Storage has progressed from being a computer system add-on to taking center stage in the organizations. On a global scale, industrialized countries led by the United States place a high value on data storage and backup technology and make extensive use of it. The connection between servers and tape drives has surpassed 60%. In China, only about 15% of servers are connected to backup devices, and most servers’ data is at risk of being damaged or lost at any time. As a result, determining how to efficiently handle stored data and ensuring its security has become a pressing issue.
Cloud storage
Cloud storage is a novel concept that has grown out of the cloud computing concept. It refers to a system that uses application software to connect a large number of different types of storage devices in a network to provide data storage and business access via cluster applications, grid technologies, distributed file systems, and other approaches. Cloud storage is essentially a utility service that offers multiple users with a shared storage pool that can be accessed through the internet. Cloud storage is similar to SaaS services in terms of business delivery, except that cloud storage provides storage management and services. Cloud storage pools are adaptable, allowing them to be readily expanded or adapted to meet the demands of customers. The term “cloud storage” refers to the pinnacle of storage technology, which is divided into three categories: organizational structure, data optimization, and security management.









Leave a comment