Latest Posts
SSD Drive vs SD Card: Comparison and Difference
Introduction
Knowing how SSD Drive Vs SD card compare makes all the difference whether you need extra space for your computer or phone.
SSDs offer speed and durability for computers and gaming. On the contrary, SD cards, being portable, are ideal for cameras and mobile devices. Let’s explore more about them.
Overview of SSD Drive vs SD Card
Solid-State Drives
Developed in the late 1970s, SSDs gained real traction years later. The rise of NAND flash memory allowed for faster data access than traditional hard drives. As technology advanced, costs decreased, making SSDs available to everyone. Today, they are the solid choice for storage across devices, including personal computers and data centers, valued for their speed and reliability.
SSDs serve as high-speed, reliable data storage solutions across various uses. Their lack of moving parts results in quicker read and write speeds, lower latency, and better durability. Commonly found in personal computers, servers, and gaming consoles, SSDs store operating systems, applications, and large files requiring fast access. They also use less power than hard drives, making them ideal for laptops and portable devices.
SD Cards
Panasonic, SanDisk, and Toshiba launched SD Cards in 1999 for compact storage in cameras and smartphones. Initially offering just 32MB, SD cards have significantly increased capacity and speed. Now, they can handle larger files and high-quality media with formats like SDHC and SDXC. They are a trusted option for portable storage, especially for limited space.
Famous for external data storage in devices, they often hold media files such as photos, videos, and music. Their small size and ease of swapping make them ideal for storage expansion. Moreover, they are used in some embedded systems and industrial applications that require compact, removable storage.
Types of SSD Drive Vs SD Card
Types of SSDs
SATA SSDs
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment SSDs connect through the SATA interface, previously used for hard drives. They are faster than traditional drives but limited to about 600 MB/s due to the SATA III standard.
Non-Volatile Memory Express SSDs
NVMe SSDs, a significant advancement, connect directly to the motherboard using PCIe. It allows speeds that often exceed 3GB/s. Their lower latency and higher bandwidth make them the top choice for peak performance.
External SSDs
For additional storage that doesn’t require opening your device, external SSDs are a smart solution. They connect through USB, Thunderbolt, or similar ports. They typically underperform than internal SSDs, but they still offer better speed than standard external hard drives.
Types of SD Cards
SDHC, SDXC, and microSD
SD cards have several types for varying storage requirements.
-
-
- SDHC cards offer storage from 4 GB to 32 GB.
- In contrast, SDXC cards support larger sizes, from 32GB to 2TB.
- microSD cards function as compact counterparts to standard SD cards. They offer diverse storage capabilities with SDHC and SDXC formats.
-
UHS-I and UHS-II
UHS refers to Ultra High Speed, a measure of SD card speeds.
-
-
-
- UHS-I cards can handle speeds up to 104 MB/s.
- UHS-II cards are quicker, reaching 312 MB/s.
- With an extra row of pins, UHS-II cards ensure faster data transfer and work with compatible devices.
-
-
SSD Drive vs SD Card: Which Is Best For You?
Performance Differences
-
-
-
-
- NVMe SSDs are the fastest, easily surpassing SD cards in speed and access times. SATA SSDs offer good performance but don’t quite match NVMe speeds.
- In contrast, SDHC and SDXC cards offer moderate speeds, with UHS-II cards performing the best.
- If you need storage for operating systems or software, go with SSDs. For portable devices, SD cards are the way to go.
-
-
-
Cost Variations
-
-
-
-
- On the cost front, SATA SSDs are typically less expensive than NVMe models, which makes them a solid option for budget shoppers. SD cards, especially SDHC versions, usually cost less than SSDs.
- However, high-performance SDXC and UHS-II cards can get near the lower end of SATA SSD pricing. You should carefully consider your storage requirements and budgets when choosing.
-
-
-
Use Cases for SSD and SD Card Types in Various Applications
-
-
-
-
- In personal computers and laptops, SATA SSDs replace old hard drives effectively. They lead to faster boot times and quicker app launches. This makes them suitable for everyday tasks and gaming while being budget-friendly.
- Gamers enjoy reduced load times and easy data access with NVMe SSDs, enhancing their gameplay. Content creators benefit from their fast data transfers and smooth playback. They also improve multitasking and facilitate quick access to large datasets in data science and software development.
- For those capturing images and videos, external SSDs are excellent for large files. Their rapid data transfer and easy USB or Thunderbolt connections allow backups and device migrations.
- Digital cameras benefit from SDHC cards, which hold enough high-quality photos and videos. Many camcorders and budget recording devices depend on them for standard-definition video.
- For photography and videography experts, SDXC cards easily accommodate high-resolution photos and 4K videos. Their larger storage and fast write speeds are perfect for long shooting periods. Nintendo Switch players also use SDXC cards for additional game storage.
- microSD cards hold apps, photos, and videos for smartphones and tablets, allowing users to cope with internal storage limits. Drones and action cameras also rely on their compact size and HD recording capability.
- UHS-I cards are suitable for mid-range cameras and standard video recording. UHS-II cards cater to high-performance cameras, offering quick data transfer for fast action and 4K video.
-
-
-
Pros and Cons of SSD Drive VS SD Card
Pros of SSD
-
-
-
-
-
- SSDs have gained popularity for their impressive speed, especially the NVMe types. They enhance system performance and reduce loading times for apps and games.
- Their lack of moving parts makes them tough and resistant to shocks. SSDs typically last longer, ensuring reliable performance.
-
-
-
-
Cons
-
-
-
-
-
-
- On the flip side, SSDs can be pricey, especially NVMe models. This higher cost might deter budget-conscious buyers.
- Many internal SSDs also have limited upgrade options, so it’s vital to consider future storage needs.
-
-
-
-
-
Pros and Cons of SD Cards
Pros of SD cards
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- SD cards are portable and lightweight, and their lower cost makes them affordable for casual users.
- Plus, many devices support SD cards, allowing for easy storage expansion without modifying internal storage.
-
-
-
-
-
-
Cons
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- However, SD cards generally offer slower speeds than SSDs, affecting data transfer and performance with larger files.
- They tend to be less durable, risking damage and wear that can lead to data loss.
- Their lower write endurance can also impact long-term reliability with frequent use.
-
-
-
-
-
-
Final Thoughts
Choosing an SSD or an SD card is about what fits your storage needs best.
NVMe SSDs shine with their speed, making them suitable for gaming and content creation where quick access is essential.
In contrast, SD cards, especially SDXC and UHS-II, offer adaptable storage for cameras and smartphones. They are great for holding photos, videos, and applications without needing SSD speeds.
Keep performance, capacity, and cost in mind when you choose. The right storage option will boost your device’s efficiency.
FAQs
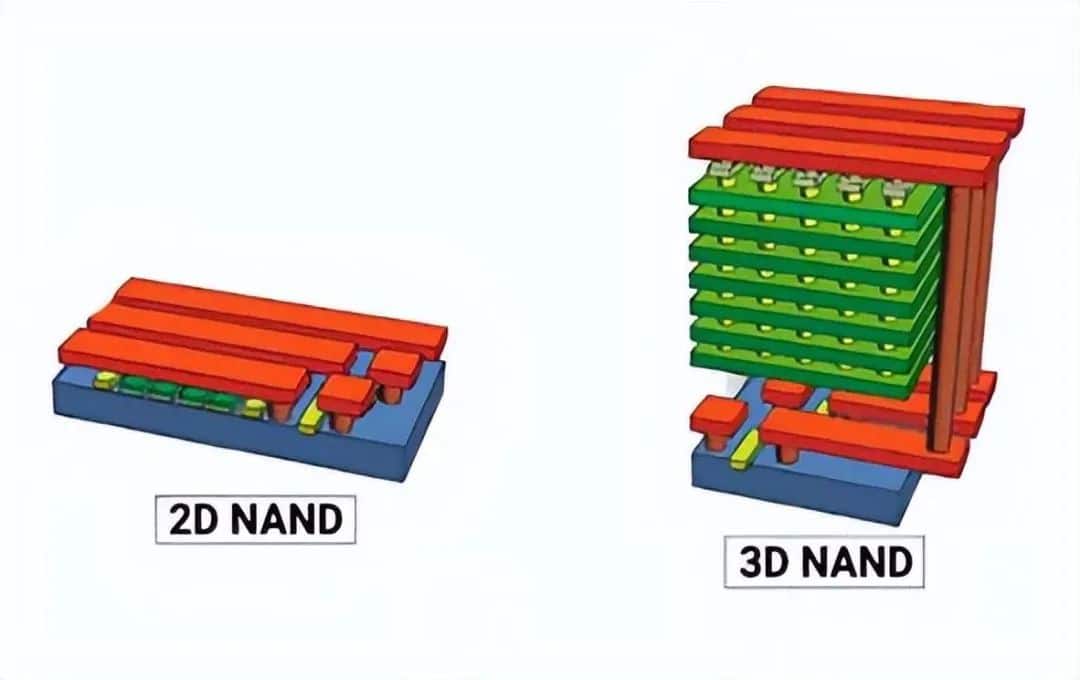
What NAND flash types do SSDs use?
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- SLC: One bit of data per cell. Fast and durable, great for enterprise use.
- MLC: Two bits of data per cell. Ideal for consumer SSDs with balanced performance.
- TLC: Three bits per cell. Offers a good amount of storage for casual use at a lower price.
- QLC: Four bits of data. It maximizes storage but is slower and less durable.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
What are speed classes and UHS ratings in SD cards?
SD cards have speed class ratings that show their minimum write speeds. The classes include:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Class 2: 2 MB/s.
- Class 4: 4 MB/s.
- Class 6: 6 MB/s.
- Class 10: 10 MB/s.
- U1: 20 MB/s.
- U3: 30 MB/s.
-
-
-
-
-
-









Leave a comment