Latest Posts
SIM Card Vs SD Card: Can They Be Used In The Same Way?
Introduction
SIM card vs SD card are essential in our devices, each serving unique functions. They look similar and can be found together, but their uses are distinct. Therefore, this guide clarifies what each card does, helping you avoid confusion and make rational decisions.
Overview of the SIM Card vs SD card
Subscriber Identity Module (SIM Card)
A SIM card is a tiny chip commonly used in mobile devices. It holds user information and connects to networks. Introduced in 1991, it has been necessary with GSM networks since 1996. Transitioned from standard sizes to micro and nano formats, they now support 4G and 5G.
Secure Digital (SD) Card
An SD card is designed for data storage. First introduced in 1999, these cards were initially made for digital cameras. Also, they have grown in capacity and speed over the years. In addition, SD cards now support HD video recording and large photo storage.
Application
SIM and SD cards are common in many devices. SIM cards are in smartphones and tablets. They connect your device to cellular networks. Thus, this connection is essential for calls and mobile data access.
SD cards are used in different devices to enhance storage. They help store more photos, videos, and apps.
Functions
Sim Card
- A SIM card connects devices to mobile networks.
- It stores user information securely, including phone numbers.
- This connection lets you make calls and send texts.
SD Card
- An SD card serves as a storage solution.
- It saves different data types, like images, videos, music, and apps.
- It helps you keep your device data organized.
SIM card vs SD card: Why Are Users Confused?
Key Differences
An SD card is used to store files such as photos, videos, and documents. A SIM card, however, is focused on connectivity. It links your mobile device to a network for calls and mobile data.
The physical shape of both cards is different. SD cards are rectangular and large, while the latest SIM cards are smaller, with standard, micro, and nano options.
Common Misunderstandings
SIM and SD cards often create confusion because of their similarity, but they have distinct roles. Users sometimes think they serve the same function simply because they fit into digital devices.
The presence of both card slots on their devices creates another misconception. Therefore, they might think the cards are interchangeable due to their proximity. As a result, it can result in improper usage, causing issues with the device’s performance.
Types of SIM Cards and SD Cards
Types of SIM Cards
The type of SIM depends on its storage and the technology it supports.
- Standard SIM (Mini-SIM), a pioneer SIM card only found in some older mobile phones, is now obsolete for new devices.
- Micro SIM allows the chip to be smarter in size than it had been before. It was used in devices, including the iPhone 4, offering standard SIM card features in tiny form.
- Nano SIM: Since 2012, the Nano SIM has been significantly smaller. New smartphones, including the iPhone and modern Android models, use it as a standard. This way, users may get more space for advanced hardware.
- Embedded SIM, or eSIM is integrated directly within devices and not in traditional SIM cards. It allows users to change networks without requiring a physical card. Such integration is becoming common in wearables, smartphones, and IoT, supporting multiple profiles on one device.
- Universal Integrated Circuit Cards is also known as UICC. With the addition of 3G, 4G LTE, and 5G, this advanced SIM card supports different network carriers to offer secure mobile banking and web browsing. Found in modern smartphones, they offer contactless payments and identity verification features.
| SIM Card Type | Dimensions (mm) | Dimensions (inches) |
| Standard SIM | 85.60 x 53.98 | 3.37 x 2.13 |
| Mini SIM | 25 x 15 | 0.98 x 0.59 |
| Micro SIM | 15 x 12 | 0.59 x 0.47 |
| Nano SIM | 12.3 x 8.8 | 0.48 x 0.35 |
| Embedded SIM (eSIM) | Integrated | N/A |
SD Card Types
SD cards come in several types, each defined by unique technology and performance. The main categories are as given below:
- Standard SD cards, or SDSC cards, are the first type of SD card with up to 2 GB capacity. These cards use FAT16 to manage basic needs in MP3 players and cameras. However, their small size limits their current usefulness.
- High-capacity SD cards or SDHC: SDHC cards support 2 GB to 32 GB storage. They utilize the FAT32 file system for improved file organization. Thus, these cards are ideal for moderate storage tasks like recording HD videos and storing numerous photos.
- Ultra-high-capacity SD cards or SDXC: These cards have 32 GB to 2 TB storage. They use exFAT, a file system designed for bigger files, which is great for HQ videos and images. Professionals in media production often prefer them for their speed and storage.
- Specialized SD card types: Specialized SD cards include SDUC, with up to 128 TB storage capabilities. Speed classes, from 2 to 10, determine performance, while UHS cards offer top speeds of 624 MB/s for high-performance needs.
How to Use Them on Different Devices?
Using SIM Cards
- Shut down your device and use a SIM ejector tool to take out the tray.
- Place the SIM card in the tray, gold contacts facing down.
- Inject the tray and power on your device. It should automatically recognize the SIM.
- You might have to enter a PIN code to activate it.
SIM cards work in tablets and smartwatches, not just phones. These devices have similar SIM card insertion processes.
Using SD Cards
- Switch off the device and eject the card slot, usually on the side or back.
- Insert the SD card into the slot carefully and put the tray back, until it clicks in place.
- Once done, turn the device on, and it should recognize the card.
Note: Formatting an SD card after inserting it ensures smooth performance. However, it removes all data and sets it up for use. Go to storage settings, pick the SD card, and click format to erase all data.
Final Thoughts on Purchasing SIM card vs SD Card
Choose your SIM or SD card carefully by considering the key features that align with your needs.
Factors to Consider
Device Compatibility
Check the needed size, Nano, Micro, or Standard, for SIM cards. Most new phones use Nano SIMs, but older models may need other sizes.
For SD cards, ensure your device accepts the correct SD card format. Many devices support SDHC or SDXC. SDXC won’t work if it only supports SDHC. Moreover, a Class 10 or UHS card is crucial for demanding activities like 4K video or gaming.
Intended Use
Your use case matters. If you travel internationally or frequently switch networks, eSIMs provide flexibility by making network changes easier.
Consider the amount of storage and speed required for your files for SD cards. Obviously, SDXC cards are ideal for high-res media.
Quality and Reliability
Prioritize quality and reliability over cost when selecting an SD card. On this occasion, low-cost cards can cause data issues or slow speeds. Go with brands that have a reputation for reliability.
Check your device specifications to choose the best SIM or SD card and define your storage or connectivity needs.
Conclusion
Knowing how SIM and SD cards differ is vital when choosing them for your devices. With four formats, standard, micro, nano, and embedded, SIM cards link to cellular networks for calls and data. In contrast, SD cards provide storage solutions, holding photos, videos, and applications. Moreover, they have types, like standard SD, SDHC, and SDXC, each for specific storage needs. When purchasing a card, check for compatibility and consider your storage needs.

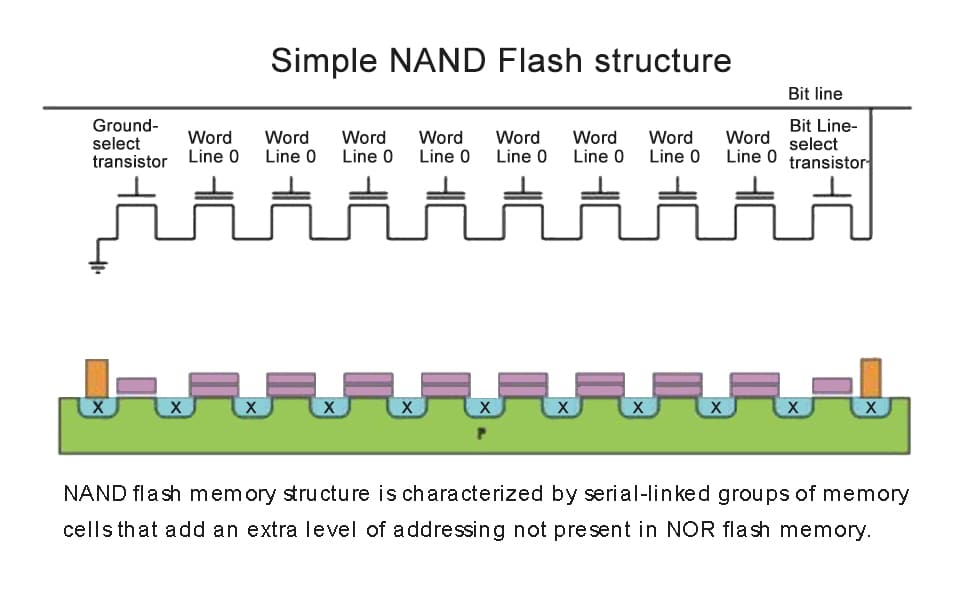
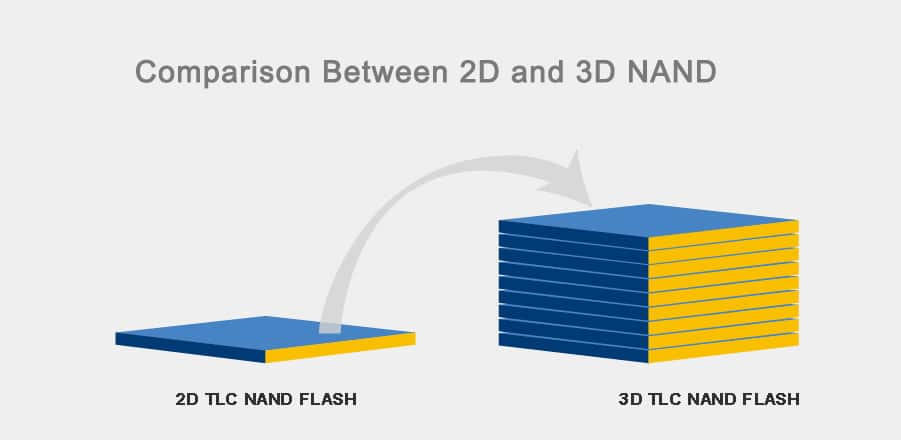
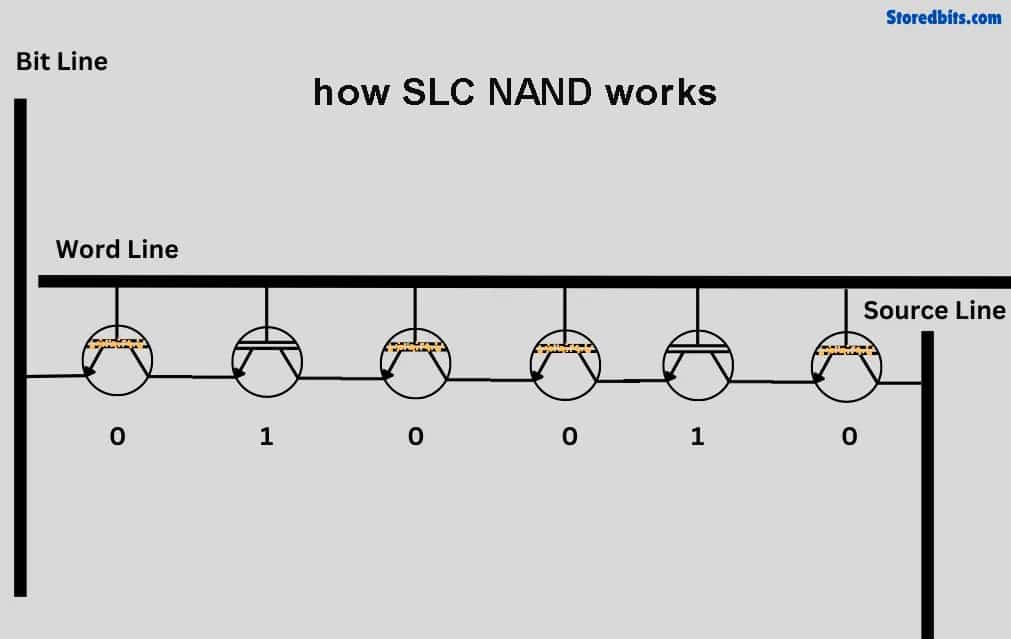




Leave a comment