Latest Posts
Is SLC Better Than TLC for Memory Cards?
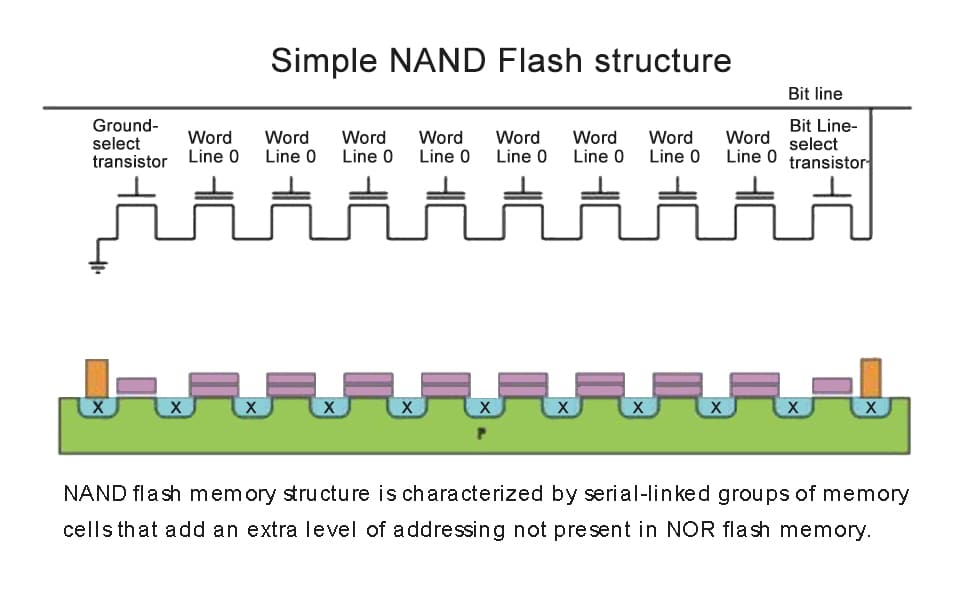
SLC and TLC: An Introduction
SLC and TLC are both NAND flash memory types that store data in distinct ways. Each type stores data differently, which impacts their performance, lifespan, and price.
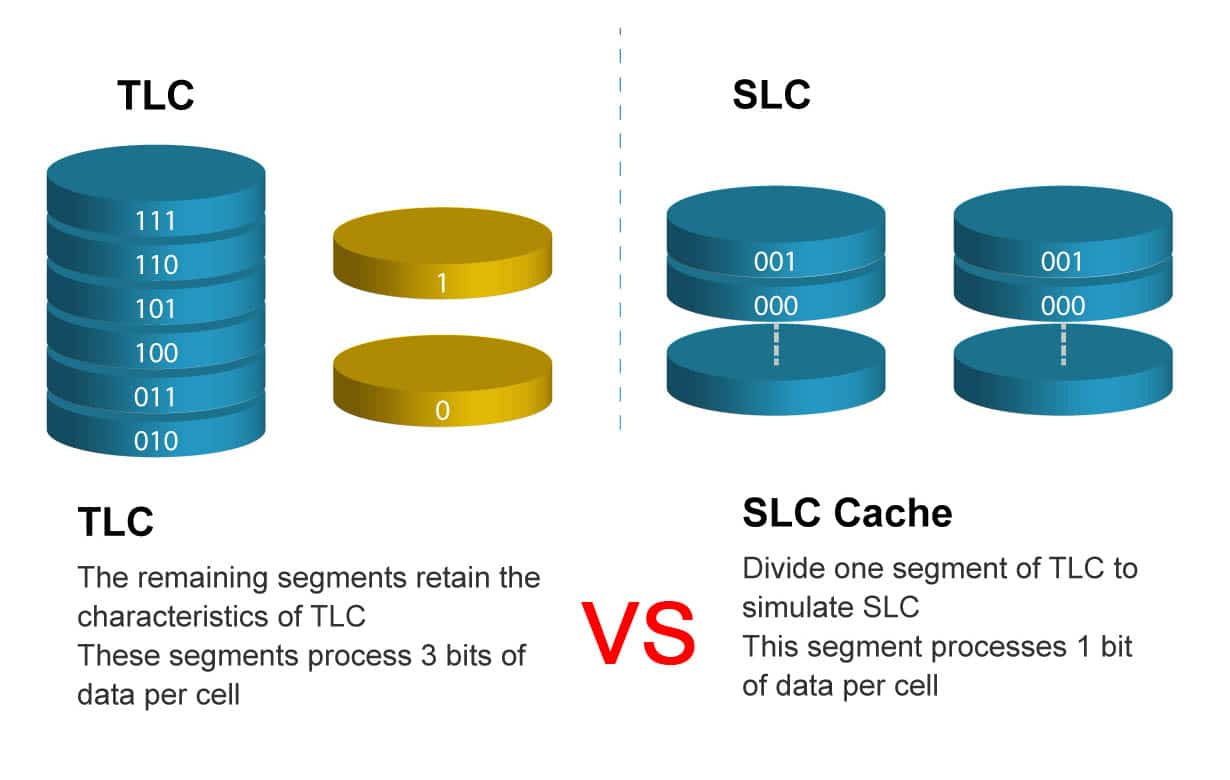
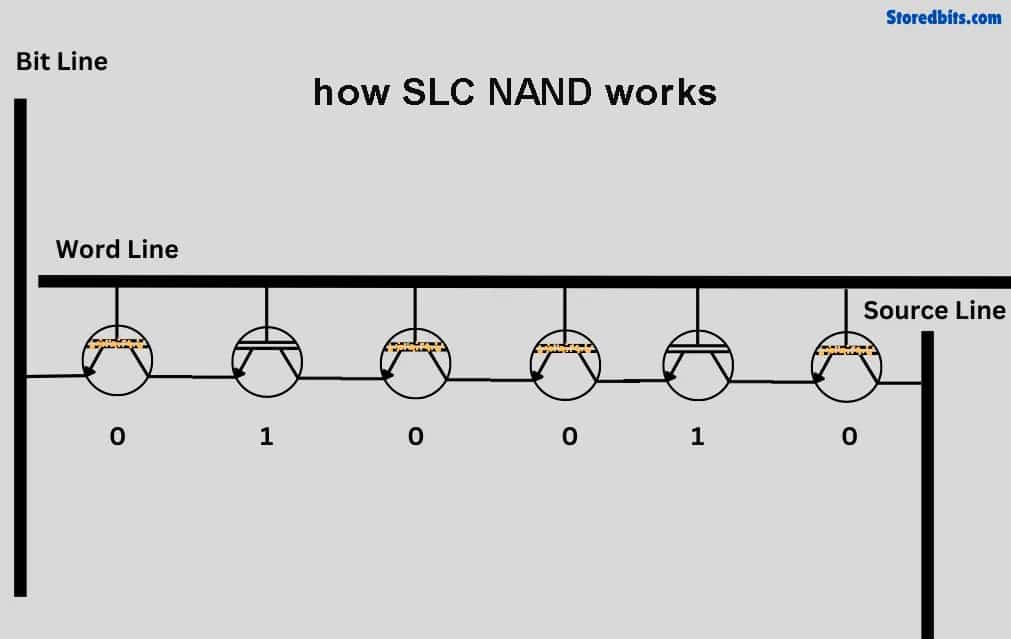
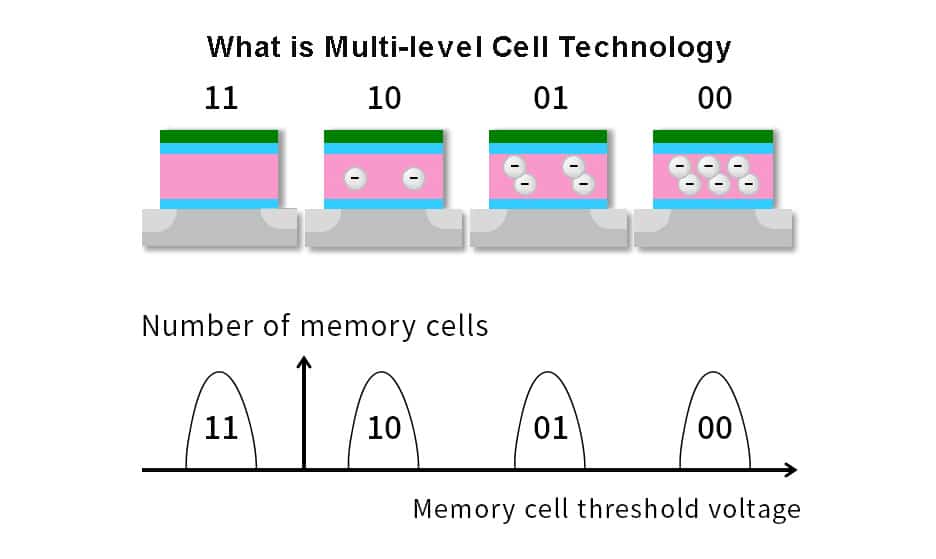
Single-Level Cell
SLC stores a single bit of data in each memory cell. This simple design leads to faster read and write speeds. It also offers greater durability because the cells experience less wear over time. SLC is commonly found in high-performance settings like enterprise SSDs, servers, and industrial equipment. However, its advanced capabilities come with a higher price tag.
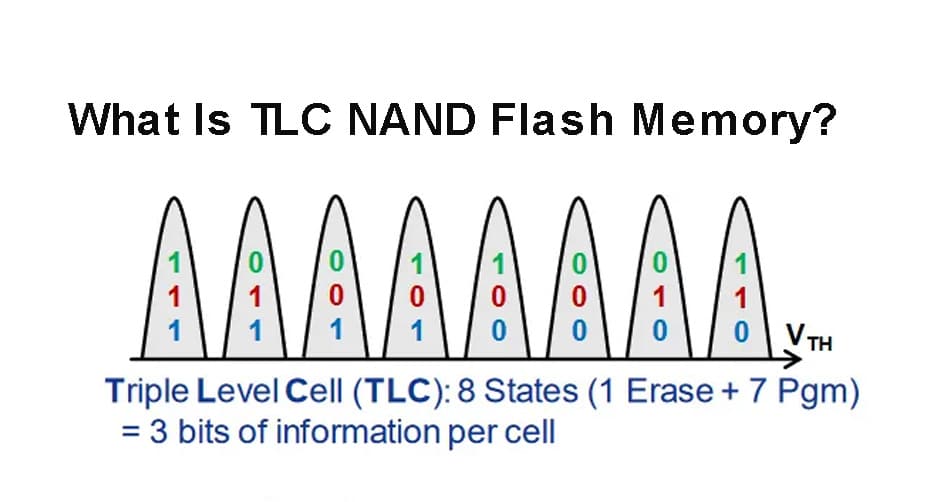
Triple-Level Cell
TLC stores three bits per cell, making it an efficient way to increase storage without using more space. It’s found in smartphones, laptops, and many consumer SSDs. The tradeoff is slower speeds and lower durability compared to SLC. It’s frequently used in budget-friendly SSDs and memory cards, offering decent performance for the price. But its lifespan tends to be shorter with regular use. This write-up will simplify these differences so you can select the right card confidently.
Key Differences Between SLC and TLC
Deciding between Single-Level Cell and Triple-Level Cell NAND flash technology can impact your memory card’s performance. Each has benefits, depending on your priorities like cost, durability, speed, and performance.
Cost
SLC memory cards come at a premium. Each cell holds just one bit, maximizing speed and durability. Yet, this design requires complex manufacturing, pushing up the price.
TLC cards, by comparison, store three bits per cell, making them easier and cheaper to produce. This high data density also allows for more storage at an affordable price, perfect for everyday users.
Life Cycle / Durability
SLC memory cards stand out for durability. Each cell holds a single bit, allowing SLC cards to handle thousands of write cycles without a noticeable slowdown. They’re perfect for intense use cases like professional video work or high-end applications, requiring stability.TLC cards, but, don’t last as long. With 3 bits per cell, they wear out quickly, especially for intensive writing tasks, such as video recording. Though TLC works well for most general uses, it may not endure as well under constant heavy use.
Speed
SLC memory cards offer faster read and write speeds due to their simple minimal design. They enable swift data access, making them ideal for handling large files like 4K videos or high-resolution photos. TLC cards work well for general use but can lag with heavy writing demands. You might notice this during large file transfers for gaming, video editing, or high-speed photography.
Performance
Known for both speed and resilience, SLC cards excel in high-demand situations. They handle intensive work, from video recording to large file storage, giving professionals reliable performance.
TLC cards are better for general use, such as saving photos, music, or videos on a phone or camera. However, they may not hold up well under demanding tasks like continuous 4K recording.
Power Consumption
SLC cards demand more power to support their high speeds and durability. This extra power use can affect battery life in devices like drones or cameras.TLC cards are more energy-friendly, needing fewer write cycles and lower power. They fit well in portable devices where conserving battery life is important.
Capacity
With smaller capacities, storing one bit per cell, SLC cards often come in lower storage sizes. It makes them suitable for users who prioritize durability over space.TLC cards can hold more data due to their three-bits-per-cell design, making them a good choice for extra storage without spending too much.
Impact of SLC and TLC on Memory Card Performance
Speed and Performance
Speed and performance in memory cards depend largely on the flash technology used. Here’s how they compare:
- Write/Read Speeds: SLC cards store just one bit of data per cell, making read and write processes faster. This gives SLC cards a performance edge over TLC cards, which manage more data per cell. For users, this means faster data transfer—key for time-sensitive tasks.
- Random Access Times: SLC cards excel at quickly accessing scattered data. This efficiency is crucial for tasks involving large files, where quick retrieval is essential. Whether you’re editing video or shooting in burst mode, SLC ensures smooth performance with minimal delay.
- Applications: SLC’s speed makes it perfect for demanding tasks:
- 4K Video Recording: Recording 4K video requires high write speeds to avoid frame drops. SLC cards keep up without interruptions.
- Large File Transfers: When transferring heavy files like RAW images or high-res video, SLC cards make it quick, saving valuable time for professionals.
Capacity
TLC provides substantial storage at a price SLC can’t match. Here’s why:
- Bits Per Cell:TLC cards use cells that store three bits, while SLC cards store only one bit per cell. This structure gives TLC cards a much higher data capacity than SLC cards of the same dimensions.
- Cost Savings:With higher data density per cell, TLC card production costs less, which can mean savings. If storage capacity matters more than speed, TLC cards provide a budget-friendly option. A 128GB TLC card often costs less than a smaller SLC card, making it great for affordable storage or backups.
SLC Vs TLC: Which is Better?
For Casual Users: TLC
For casual use, Triple-Level Cell memory is practical and cost-effective for:
- Photography & Video: Affordable with enough speed for HD videos and personal photos.
- Gaming: Suitable for mobile and console gaming, offering decent speed and storage at a low cost.
- Basic Storage: Plenty of space for files, documents, and images, perfect for non-demanding uses.
Benefits
- Large storage capacities at a lower cost.
- Suited for casual gaming, photos, and HD video storage.
Limitations
- Fewer write cycles mean reduced lifespan.
- Limited speed for professional tasks.
For Professionals: SLC
Single-Level Cell memory is well-suited for professionals requiring reliability and high-speed performance. It thrives under heavy read/write demands, especially in areas like:
- Video Production in 4K or 8K:SLC prevents frame drops, maintaining a steady recording speed for high-quality footage.
- Rapid-Fire Photography:With its quick speeds, SLC is best for photographers handling large RAW files, minimizing transfer delays.
- Data-Heavy Fields:SLC’s durability ensures consistent performance in applications needing frequent data writes, like research and data logging.
Benefits
- Exceptional durability and reliability.
- Maintains fast speeds for high-demand tasks.
Drawbacks
- Costs more per gigabyte.
- Offers less storage than TLC for a similar price.
Cost vs Performance
Picking between SLC and TLC is really a question of performance needs vs budget constraints.
When SLC Shines?
In fields needing speed and reliability, like videography, lab research, or high-speed photography, SLC’s performance and longevity are worth the extra expense. It’s an investment that supports intensive workflows.
Where TLC Fits Best?
For most people, TLC is a great fit. If you’re not working in a high-demand field, it provides solid value, offering ample storage for casual photos, videos, and everyday files.
The Future of NAND Flash Technology
Advancements in SLC and TLC
NAND flash technology is evolving quickly. SLC and TLC are improving as demand for faster, more durable memory cards rises.
SLC will continue to dominate in high-performance areas, like 4K video and professional photography. The focus will be on boosting endurance and speed while keeping costs down.
TLC will focus on maximizing storage and lowering prices. Its higher density makes it a good choice for everyday use, with manufacturers working on improving its reliability.
Emerging Technologies: QLC and PLC
Newer technologies like QLC and PLC are in development. QLC stores four bits per cell, and PLC aims to store five. These technologies offer more storage for less money but come with trade-offs in speed and durability. As they mature, they could change the memory card market, especially for budget-conscious consumers.
Trends and Predictions
In the future, mobile devices, cameras, and consoles will continue to demand more storage and faster speeds. SLC will remain important for professionals, while high-density NAND like TLC, QLC, and PLC will become more common for general consumers. Manufacturers will need ways to balance performance and price, giving users more choices.
SLC vs. TLC: Final Verdict
|
Feature |
SLC |
TLC |
|
Cost |
Higher price per GB |
More affordable |
|
Durability |
Exceptional, ideal for heavy use |
Moderate, suited for lighter use |
|
Speed |
Faster read/write speeds |
Adequate for general tasks |
|
Performance |
Optimal for high-demand tasks |
Suitable for everyday use |
|
Power Consumption |
Higher power usage |
Lower power usage |
|
Capacity |
Lower capacity per card |
Higher capacity per card |
|
Best for |
Professionals(e.g.,photographers, videographers) |
Casual users (e.g., general storage) |
SLC and TLC memory cards suit different needs. SLC is fast and durable, perfect for pros handling 4K video and large data tasks, though it’s pricier. With more storage and a lower price, TLC is a good pick for casual users storing photos and documents.
New NAND tech like QLC and PLC continues to expand storage choices, balancing cost and performance for various needs.





Leave a comment