Latest Posts
Choose the most suitable, cheapest, and best quality SSD, to get the best experience.
If you have been following the technological trends, then you will know that owning an SSD (Solid State Drive) has become a key element in buying a laptop or building a PC. Since multi-core processors and gigabytes of RAM has become popular these days, storage device performance degradation often becomes a bottleneck and hinders the overall performance of the computer. However, like many technologies, SSD has more than just a bright appearance. If you are not familiar with the world of SSD and haven’t tried it yet, then here is everything you need to make a wise decision.
Analysis of solid state drive(SSD)
SSD is actually composed of several components. One is NAND flash memory: these are the components where data is actually stored. NAND flash memory consists of several pieces of non-volatile memory and does not require power to store data. The other component is the controller, which is an embedded processor that acts as the brain of the operation. It contains the firmware that manages the reading and writing tasks of the SSD. The last component is DDR memory. Many SSDs also have a very small amount of volatile DDR memory for caching information, which essentially further improves the writing speed of the SSD. Of course, SSD also needs the kit to be embedded on the PCB board to form a complete storage system.
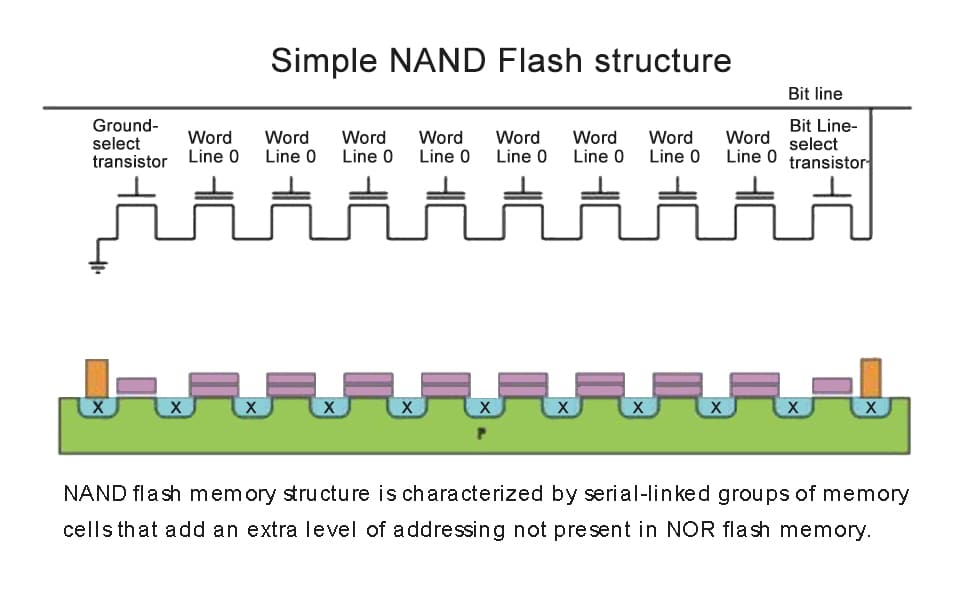
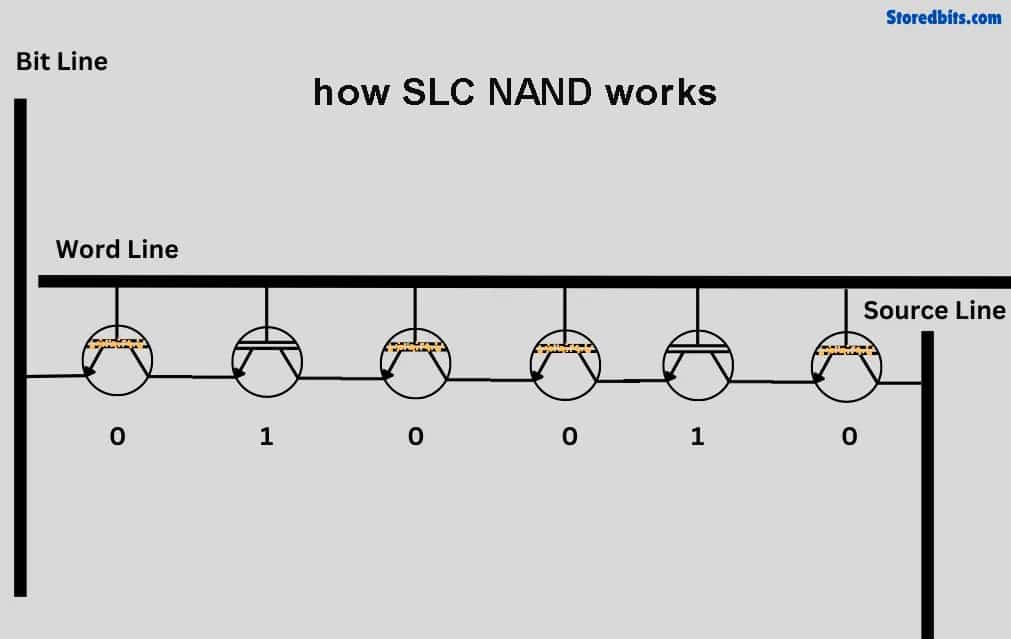
The NAND flash memory in an SSD is composed of many cells that hold information in bits that can be turned on or off. The number of bits in these cells determines the type of SSD. Each different type of SSD has different characteristics. Single-level cell SSD stores one bit in each cell. This gives them excellent performance and enhanced durability. SLC and SSD are the recommended flash memory technologies for key enterprise applications and storage services. It’s not surprised that SLC tends to be more expensive and is usually not sold to consumers.
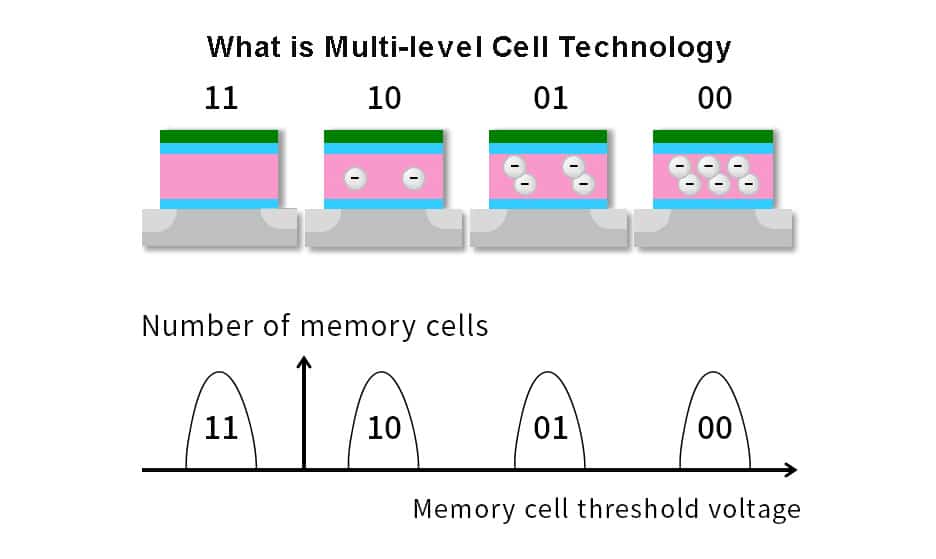
Then there is multi-level cell (MLC) SSD that can store two bits in each cell. Compared with SLC and SSD, MLC SSD can store extra bits at the expense of a slight decrease in reliability. However, this makes MLC SSDs more economical.
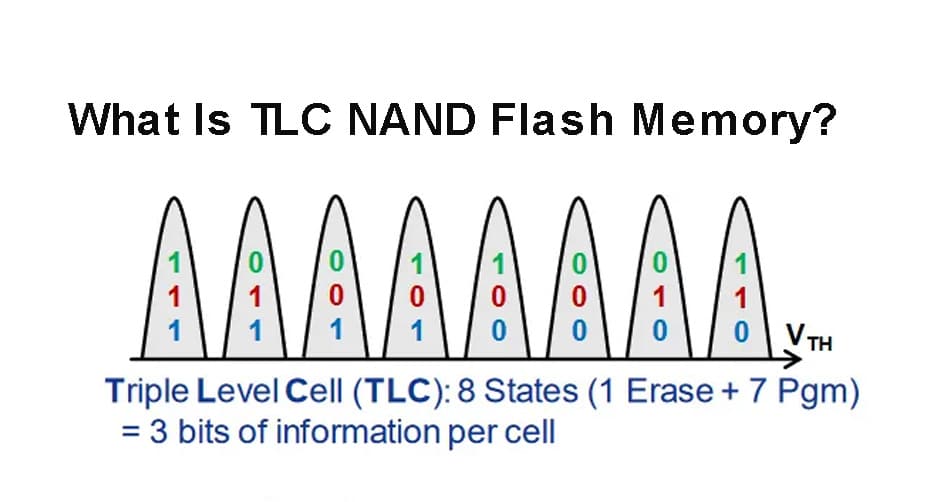
Three-level cell (TLC) SSDs are even cheaper than MLC SSDs because they store three bits per cell. Initially, TLC SSDs were usually used in cases that require large amount of reading, but due to the continuous improvements in flash memory technology, TLC SSDs are now more effective and more reliable than before, and are even used in enterprise storage applications.
In addition to the above-mentioned cell storage, the Quadro-level cell (QLC) SSD is also the latest product, each cell can store four bits. There was a time when QLC disks were not even reliable enough for ordinary desktop users.
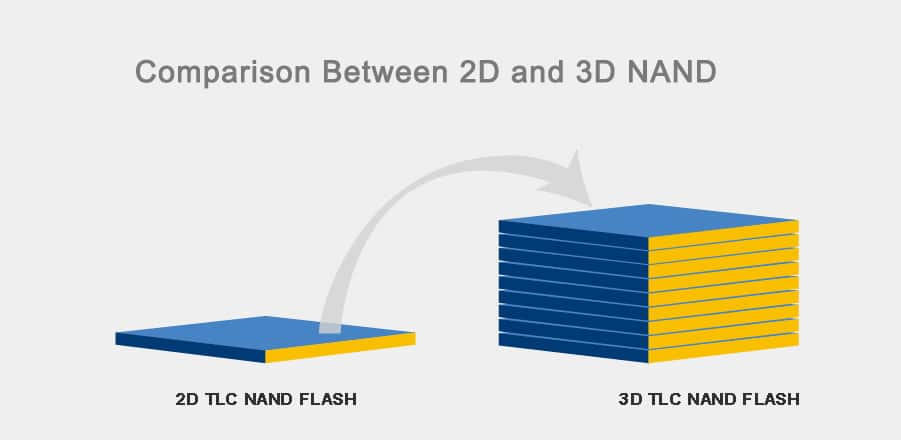
One of the biggest innovations that hit the flash memory market is 3D NAND or Vertical NAND (V-NAND). When SSD vendors tried to increase storage capacity by placing NAND storage cells close together. They found that when storage cells were too close, flash memory began to lose reliability.
SSDs have replaced traditional hard drives at an amazing speed, and traditional hard drives have been existing in the consumer storage industry for decades for good reasons:
Why are SSDs popular?
1. Excellent performance: The design of NAND flash SSD is only a magnitude faster than traditional hard drives with mechanical components. Even the first-generation SSD, which itself can never compare with the latest SSD, is several times faster than the fastest hard drive. Improved performance will transform into faster startup time and faster data transmission speed.
2. Smooth multitasking: By reducing data access time, SSD allows you to easily use multiple applications and switch between multiple applications. Background tasks such as antivirus scanning and automatic backups will have nothing to do with foreground tasks such as editing images and 4K video streaming.
3. Low energy consumption: All disks consume power. However, the mechanical components on the hard disk require more power than SSDs that only require a very small amount of current. This will help you reduce the operating cost of your PC.
4. Cooling system: As an extension of its low energy consumption, due to the lack of any moving mechanical components, SSDs can maintain a lower temperature than traditional hard drives. And since the temperature of the SSD is lower than that of the hard drive, the cooling fan does not start frequently, which helps to make the computer quieter.
5. Flexible storage: SSD has various storage sizes, ranging from several hundred GB to several TB. They come in a variety of sizes and can be used in computers with more than ten years of history with SATA ports and the latest computers with M.2 PCIe slots.
6. Better game experience: As the requirements for games are getting higher and higher, traditional hard drives are trying to keep up. Solid-state drives have faster data access speeds and are ideal for ensuring a seamless gaming experience.
Which (SSD) size do you prefer?
SSDs have different size and appearance and can run across multiple ports. Whichever drive you need depends on the device you have. If you have a computer that is relative new and has a mid-to-high-end motherboard, your system is able to integrate most modern SSDs.
On the other hand, most modern ultraportable laptops and convertibles cannot accommodate traditional 2.5-inch SSD drives. Instead, they can only accommodate the M.2 size in the shape of a chewing gum.
Solid-state hard drives are usually available in the following sizes as 2.5-inch Serial ATA (SATA). This is the most common type, similar to the hard drives of traditional laptop, and is connected via the same SATA cable. If your computer has a 2.5-inch hard drive bay and a spare SATA connector, you just need to plug it in.
There are also SSD add in cards (AIC), which are faster because these drives run through the PCI Express bus (PCIe). The AIC driver plugs into the slot on the desktop motherboard that is normally used for graphics cards. Likewise, if you have empty PCIe x4 or x16 slots on your motherboard, you can easily install them too.
Obviously, M.2 SSDs are indispensable. They are about the shape of a RAM stick, but about the size of a chewing gum. M.2 drives have become the standard for installing SSDs in notebook computers.
How to choose SSD?
1. Pay attention to flash memory particles
The flash memory particles of solid-state drives include SLC, MLC and TLC. Currently, the most widely used one is MLC. The best one is SLC, followed by MLC, and TLC is the worst.
2. How to choose solid state drive according to parameters (SSD)
Since the solid-state flash memory particles from the same brand may not have identical qualities, so be aware of the model when purchasing.
3. Brand, after-sales and quality assurance
Some brands have a three-year warranty, while others have a five-year warranty. If there is no particular belief in the brand, it is generally correct to choose one with a longer warranty.
4. Capacity
The larger the capacity, the higher the reading and writing speed; the larger the cache, the better the performance.
As for specific quality, you can ask relevant people who have used it already. According to your specific needs, choose the most suitable, cheapest, and best quality SSD, to get the best experience.





Leave a comment