What is a micro sd adapter?
Most electronic gadgets are using digital media to store data. For instance, people will use smartphones, cameras, or drones to take photos and videos. In fact, these devices normally use memory cards to load data. Therefore, memory card is a perfect media to expand the storage capacity of the devices. Micro SD card is the smallest type, you can easily use it to do file transfer or data backup. However, the memory card family has various types, how can we use Micro SD in SD card slot or USB port? The Micro SD adapter plays an important role on transforming Micro SD into various types.
What is Micro SD card?
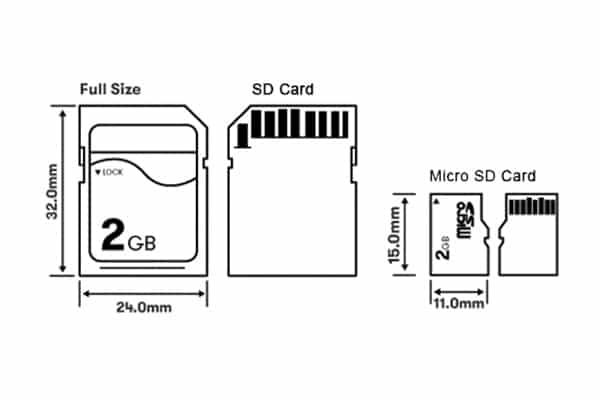
One of the smallest portable storages is Micro SD card. The physical size is 15*11mm only, the first launch of it is in 2005. People widely use it in smartphones, tablets, toys, Bluetooth speakers and the other electronical devices. The presence of Micro SD caters for the limited space in the equipment, also, it can slip into an existing SD card slot with Micro SD adapter. Let’s take a deep tour on Micro SD firstly.
| Form Factor | Capacity | ||||
| SD | Custom Sticker Size: 20x25mm (mm) / 0.78 x 0.98 inches | SD | SDHC | SDXC | SXUC |
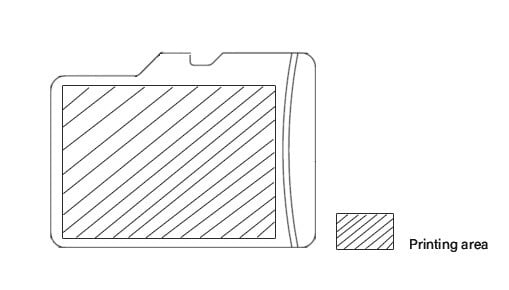
|
up to 2gb | >2gb to 32gb | >32gb to 2tb | 2tb to 128tb | |
| Microsd | print area(15*11*1 (mm) / 0.04 x 0.59 x 0.43 inches) | |
|
|
|
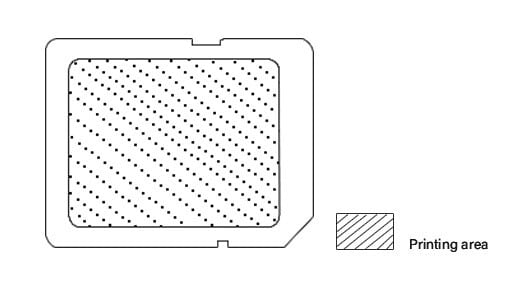
|
Write Speed >2-6mb | Write Speed >10-20mb | Write Speed >20-90mb | Write Speed >90mb | |
The Type of Micro SD card
- Micro SD – the basic type is available from 128MB to 2GB
- Micro SDHC – it represents high capacity of Micro SD, the capacity supports from 4GB to 32GB
- Micro SDXC – it refers to Micro Secure digital extreme capacity, the density can hold between 32GB and 2TB
Speed class
- Class grade – there are three ratings within the Class. Class 4 tells the minimum write speed of 4MB/s. Therefore, Class 6 and class 10 indicate the minimum write speed at 6MB/s and 10MB/s
- UHS rating – this is ultra-high speed class. The main rating of it is U1 and U3, the write speed is 10MB/s and 30MB/s at least.
- Video speed class – this feature represents higher video resolution. The micro-SD cards wearing this standard can support and capture 4k or higher resolution videos. V30, V60 and V90 are the main types.
What is Micro SD adapter?
This adapter is a device to read Micro SD in computer, tablets, cameras, or the other equipment. The main function of it is to use Micro SD card in electronic gadgets without Micro SD slot. In fact, people love buying multi-functional products, the best sale always belongs to them. Therefore, memory card adapter is to provide these extra works at lower cost. For example, you need to upload 1080p photos from your Micro SD card to laptop. The fastest way is to connect this media card with laptop, however, there are only USB ports there. How can we resolve it? Obviously, Micro Sd reader can help you out.Besides it, this adapter accessory is cost effective. Users may purchase various types of memory cards or USB sticks for wholesale order, as they need them to cater for different devices. However, it is inconvenient to bring so many kinds of memory media in one time. Thus, the presence of card adapter delivers portability and low cost.
The types of Micro SD adapter
There are three kinds of adapters.
- Micro SD to SD adapter
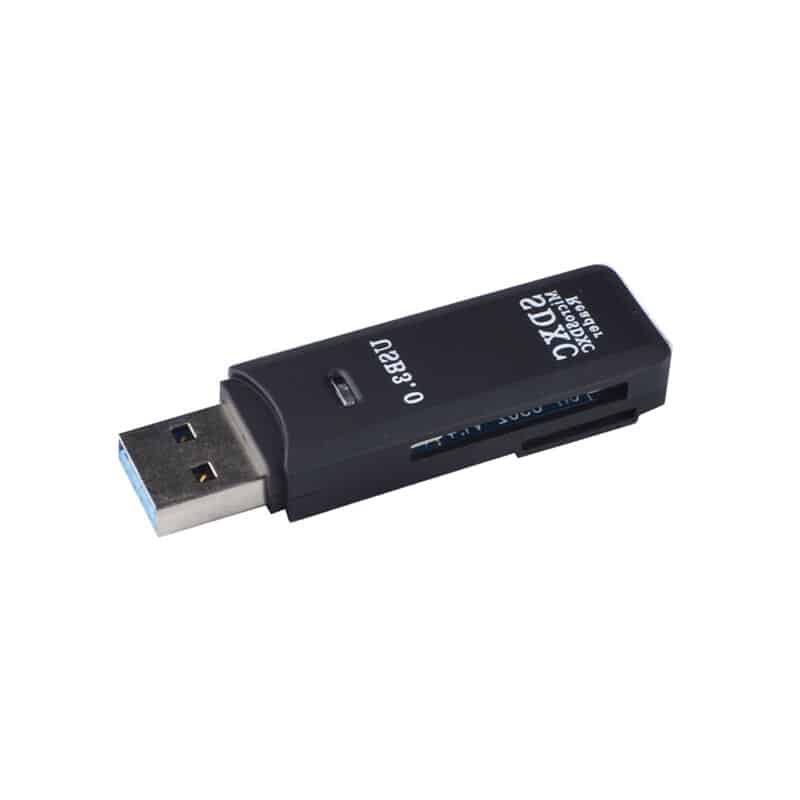
- Micro SD to USB drive reader
- Micro SD to Type C reader
The most famous one is the SD shape adapter, no matter the size or design is fully same as standard SD card. As most cameras are using SD card for storing photos and videos, this adapter can turn Micro SD into SD Card at once. When using this adapter, you need pay attention to the contact points, it will work functionally after correct connection.

Next one is USB drive reader. This is designed for the devices with USB port but no Micro SD slot. As if you need to read Micro SD in laptop or PC, this adapter will be a perfect choice. The function is same as standard USB drive, which supports plug and play.

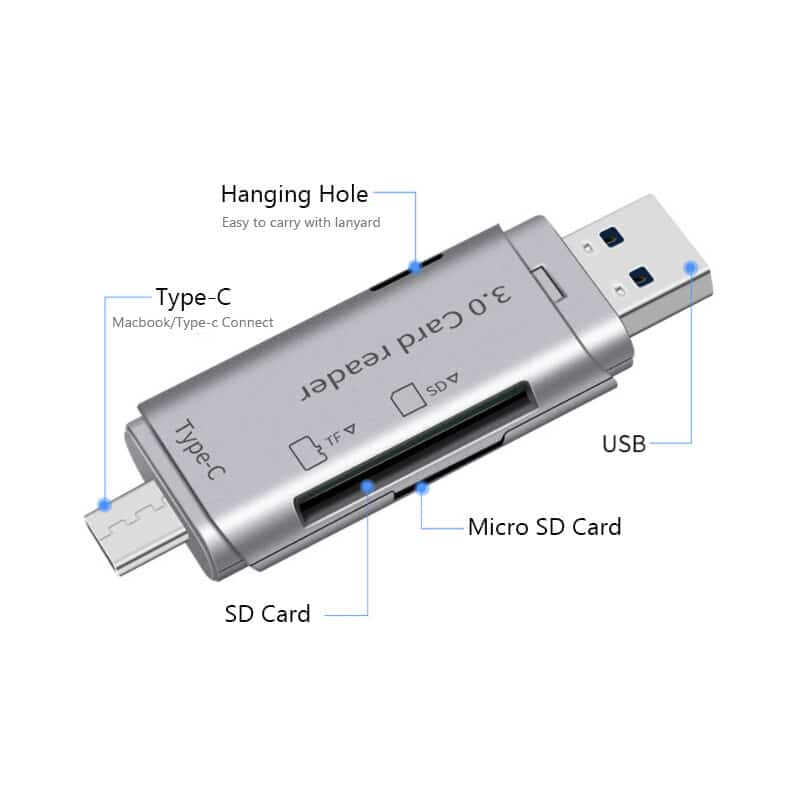
The latest one is Card reader for Typec. In other words, we can call it as OTG USB reader. People can use it to connect with tablet, smartphone and the other equipment with Typec port. In fact, this accessory offers a data bridge between Micro SD and phones.

How to make good purchase on Micro SD adapter?
This accessory is easily found in market. However, the quality is hard to judge. Therefore, the source of purchasing reliable adapter is the key.
- Brand supplier – Sandisk, Toshiba, Samsung
- OEM Factory with stable supply
- Online wholesaler with long warranty
Firstly, ordering with brand supplier or OEM factory MRT is a way to avoid any frauds. Also, sample orders are necessary prior to any big orders, you can test the contact part that will affect the function directly.Furthermore, there are many online wholesale stores for memory card accessory. MRT memory store is a trustable supplier, which has own production line and QC team. In addition, most of the products can support 5 years warranty. After sales service is the most valuable consideration for final purchase. All in all, price is important for a good purchase, but the quality and service are a foundation of long-term cooperation.
Final thoughts
No matter you need Micro SD adapter in SD style or USB stick, this small gadget helps Micro SD card achieve a perfect transformation. As if you are in low budget, this accessory definitely is a nice option to bring you multi functions.