What Is NAND Flash Memory?
You probably use NAND flash every day without even realizing it. It’s tucked inside your phone, USB drive, SSD, and digital camera. It stores your photos, videos, apps, and operating systems. Within just a few years, it has rapidly transformed storage. It’s not just about saving files anymore. NAND flash is at the center of how modern devices work.
This guide explains NAND flash memory, how it works, what makes it different from other types of flash, and where it’s headed next. If you’re looking for a clear, no-fluff explanation, you’re in the right place.
What Is NAND Flash Storage?
NAND flash is a nonvolatile storage type that keeps data even when the power is off. It’s made using floating-gate transistors arranged in a grid. Each cell in that grid holds data, usually one or more bits.
What makes NAND flash special is its compact and fast performance. Unlike traditional spinning hard drives, it has no moving parts, so it’s quicker, quieter, more energy-efficient, and more durable.
NAND flash is used in smartphones, solid-state drives (SSDs), USB sticks, SD cards, and tablets. If a device stores data and boots quickly, it likely uses NAND flash.
How NAND Flash Works
Basic Structure and Operation
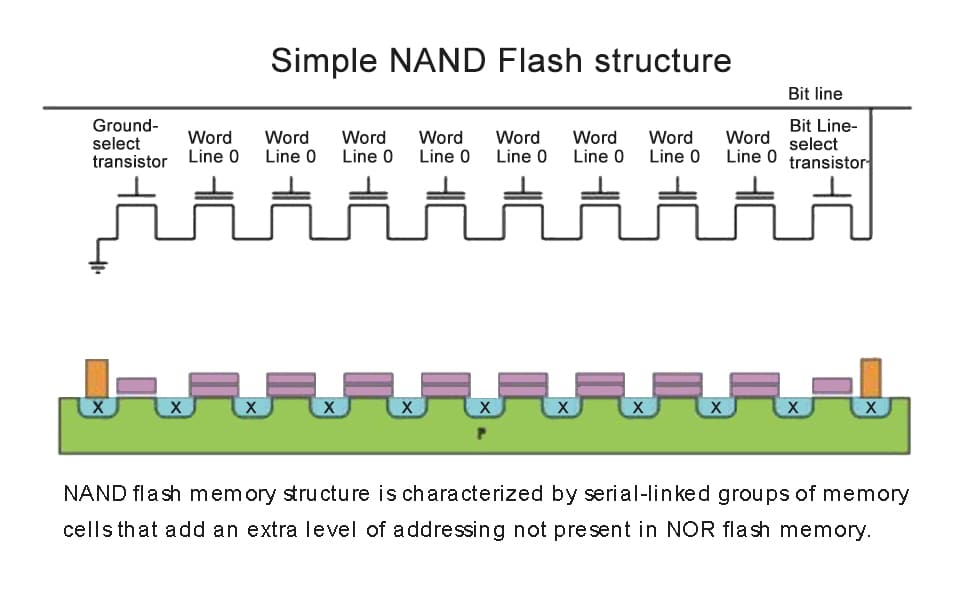
At the heart of NAND flash are memory cells made from transistors. Each cell stores a charge representing a bit—or multiple bits—of information.
These cells are organized into pages (usually 2KB to 16KB in size), and pages are grouped into blocks. Here’s the catch: you can read or write to a page, but to erase data, you need to erase the entire block. This limitation is inherent in NAND’s design.
Writing to NAND involves applying a voltage to trap electrons inside the transistor’s floating gate. The amount of trapped charge changes the resistance, which can be read as data (0s and 1s).
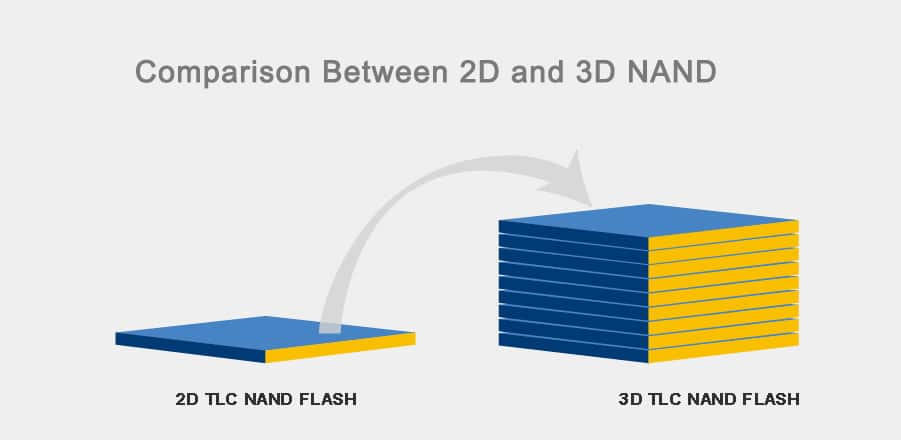
NAND flash is also layered. Newer 3D NAND stacks layers of cells vertically to fit more data into the same footprint.
Why It Works So Well
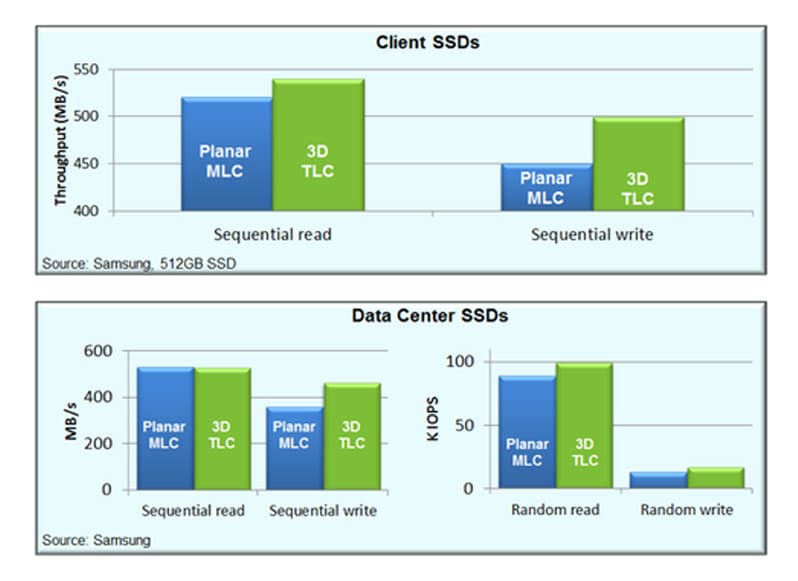
NAND flash storage offers an efficient balance of size, speed, and endurance, making it a practical choice across various storage applications. It’s faster than traditional hard drives for most tasks and shock-resistant, which makes it ideal for mobile devices.
But it has limits too. Flash cells wear out over time—each block can only be erased and rewritten so many times. That’s why flash controllers use wear-leveling algorithms to spread out the usage.
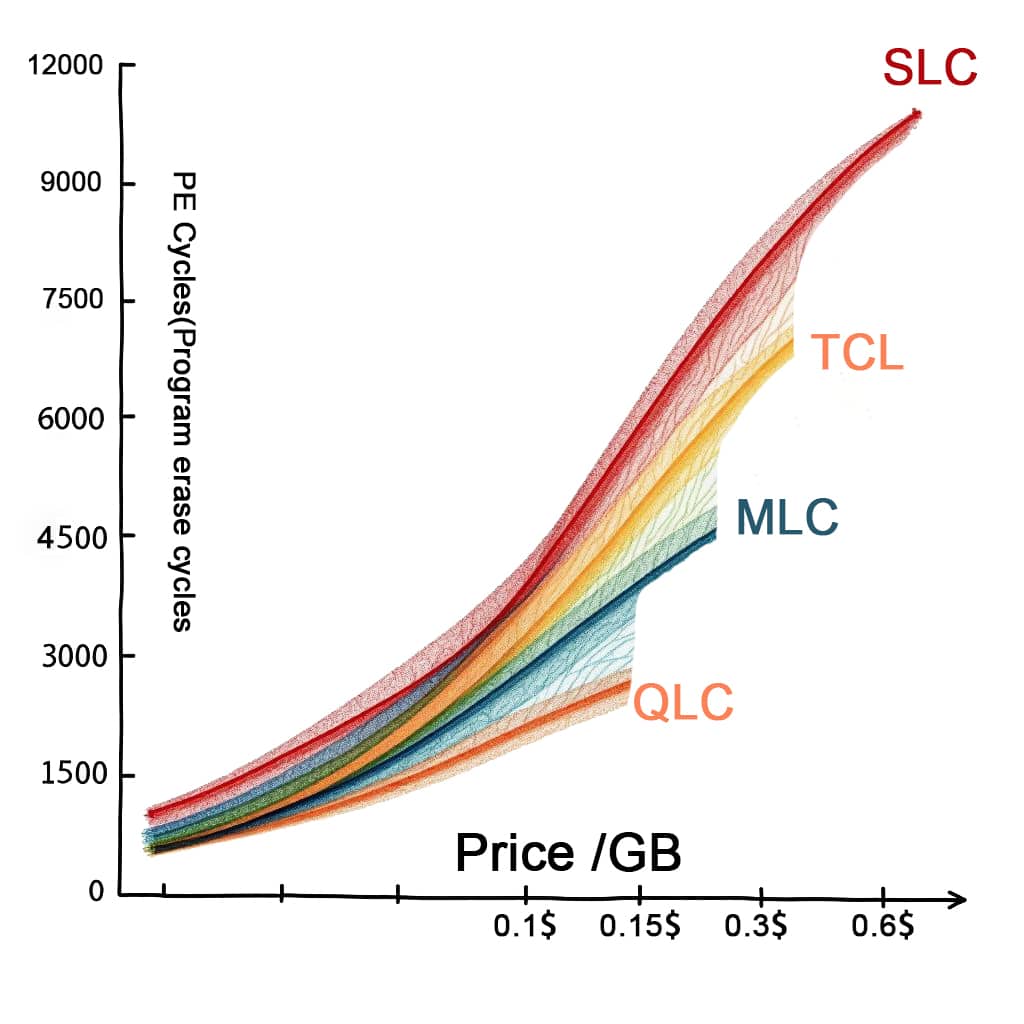
Also, the more bits stored per cell, the cheaper it gets—but the trade-off is lower endurance and slower speeds. That leads us to the next section.
Types of Flash Memory
Flash memory mainly comes in two forms: NAND and NOR. Both are non-volatile, but they work differently and serve different purposes.
NAND Flash
NAND is built for speed and storage density. It works best when reading and writing large amounts of data. There are several subtypes, and each has its use case.
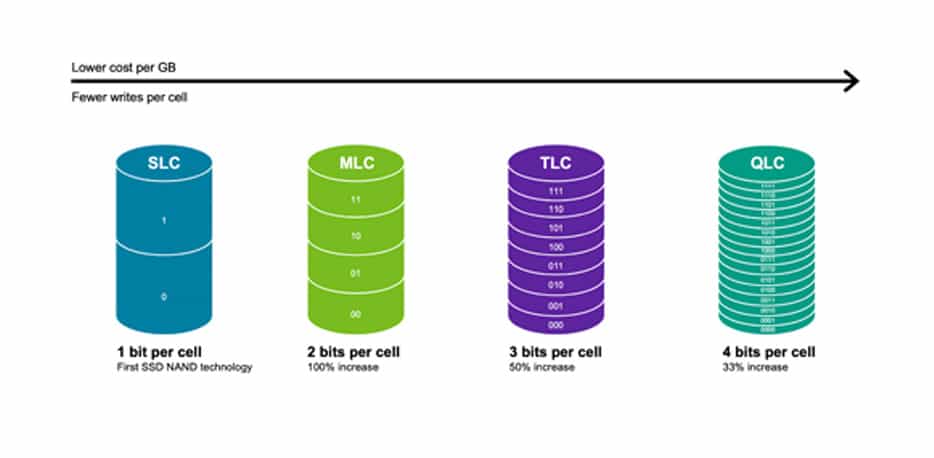
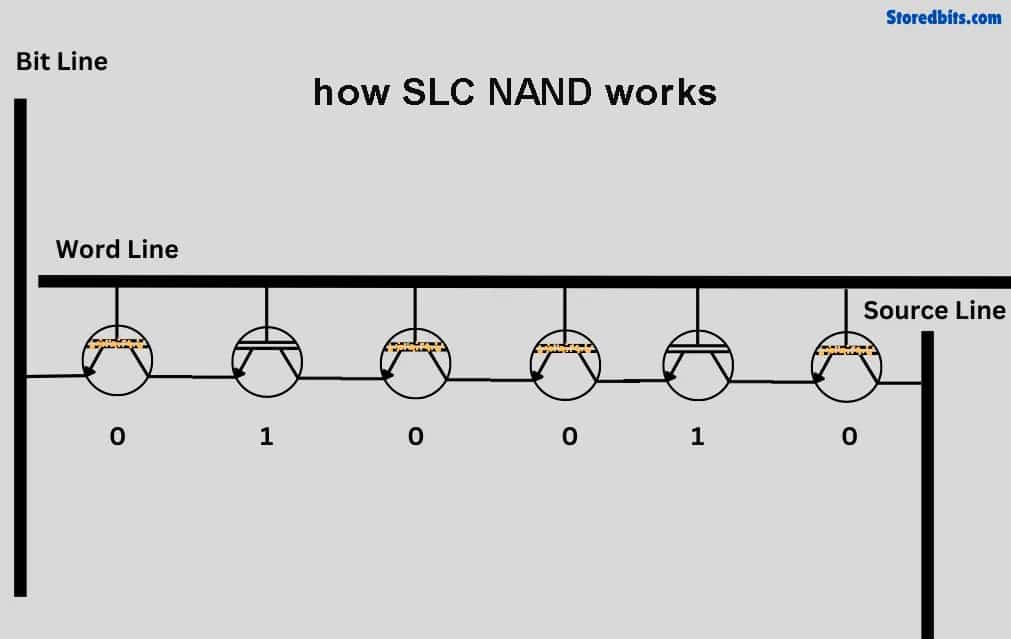
SLC (Single-Level Cell)
Stores 1 bit per cell. It’s the fastest and most durable. SLC has been used in mission-critical systems that require high speed and strong reliability. It’s expensive, so you won’t find it in consumer devices.
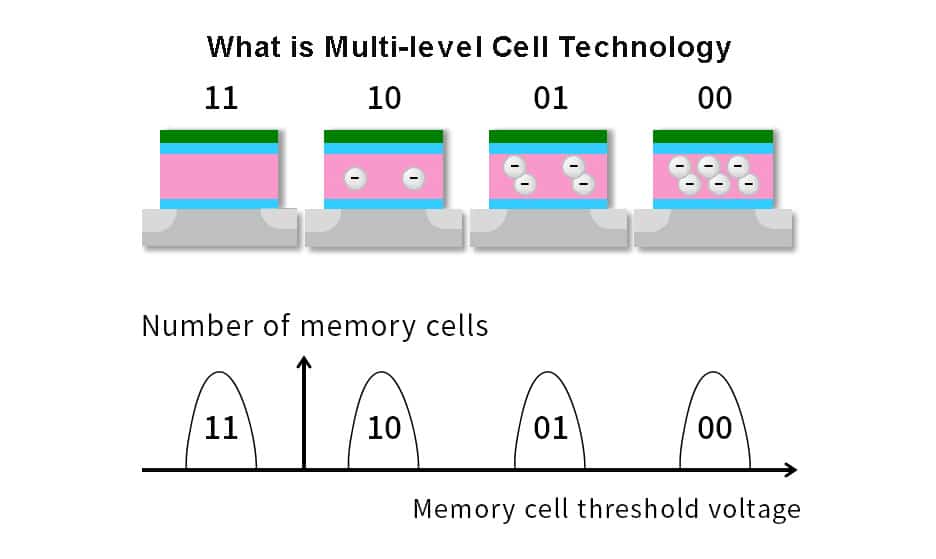
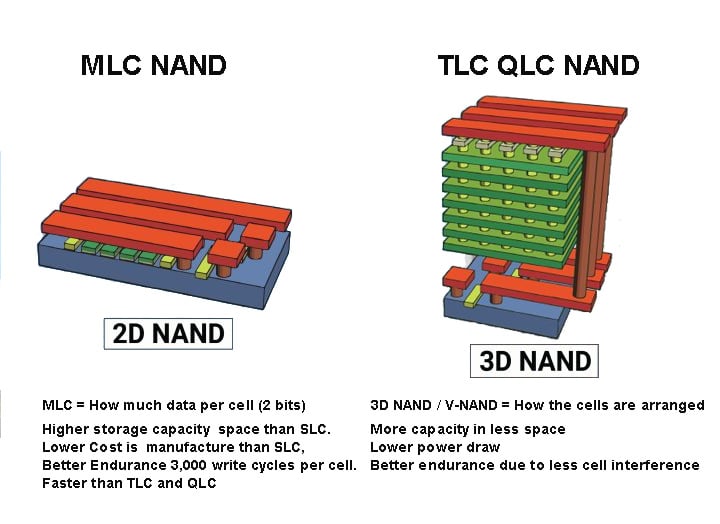
MLC (Multi-Level Cell)
Stores 2 bits per cell. A good balance between cost, speed, and durability. Often used in mainstream SSDs.
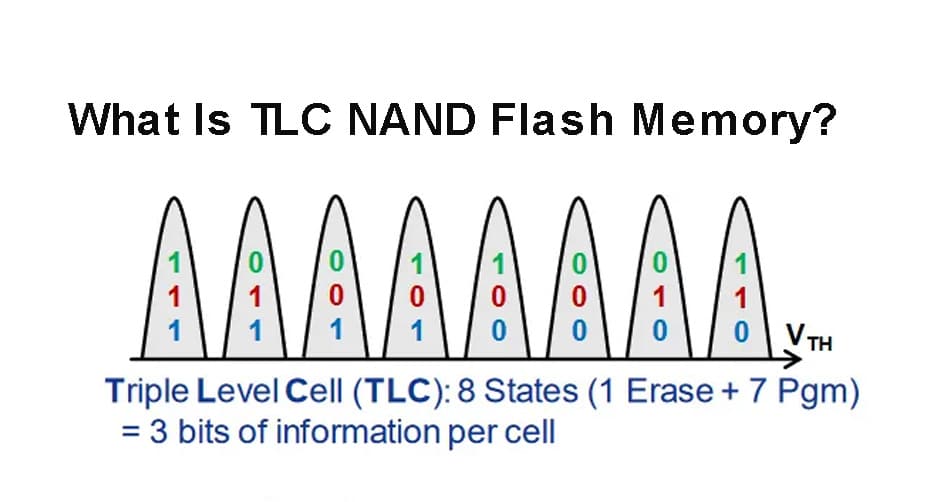
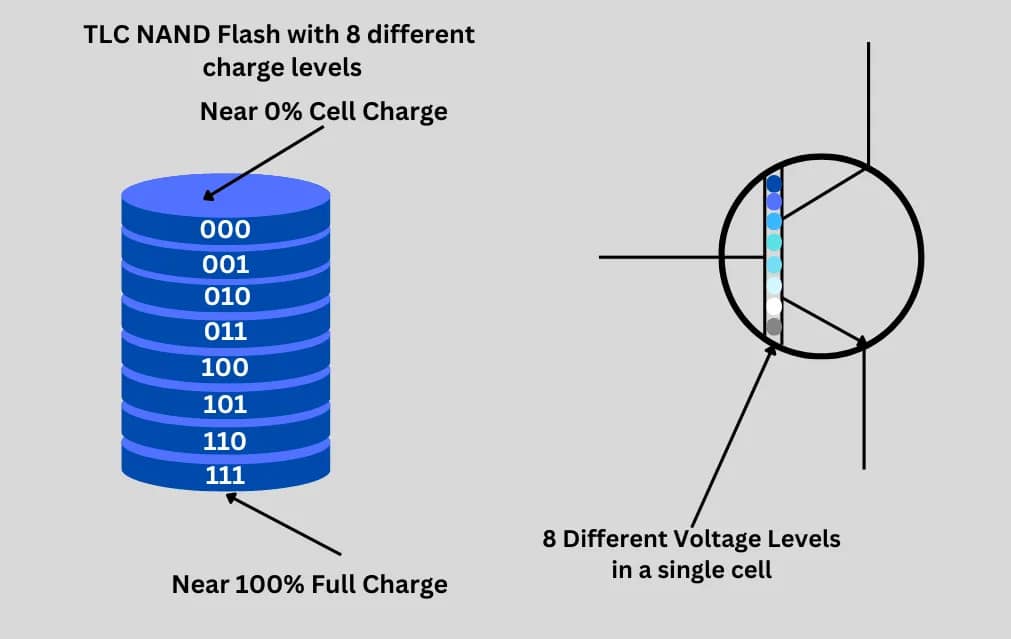
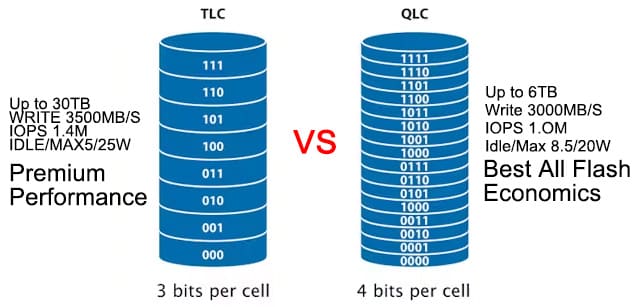
TLC (Triple-Level Cell)
Stores 3 bits per cell. More affordable, but slower and wears out faster. It’s common in consumer-grade SSDs, memory cards, and USB drives.
QLC (Quad-Level Cell)
Stores 4 bits per cell. Economical and denser, but not as fast or long-lasting. Best for storage-heavy tasks like archiving or write-once-read-many workloads.
3D NAND
Instead of laying cells flat, 3D NAND stacks them vertically. That means more storage in less space. It’s now standard in most SSDs.
NOR Flash
NOR flash offers random-access reading and individual byte-level access, making it perfect for storing firmware in devices like routers or embedded systems.
It’s slower for writing and doesn’t scale as well in size. But it boots up instantly and allows direct code execution, which NAND can’t do.
Serial NOR
Often used in IoT devices or microcontrollers. It uses fewer pins and takes up less space.
Parallel NOR
Used where speed is slightly more important than footprint, such as in high-end embedded systems.
NAND vs. NOR Flash Memory: A Quick Comparison
Feature |
NAND Flash |
NOR Flash |
Data Access |
Sequential (block/page level) |
Random (byte-level) |
Speed |
Faster for writing and large file transfers |
Faster for read-only or small code execution |
Boot Capability |
Cannot execute code directly |
Can execute code directly from flash (XIP) |
Write/Erase |
Must erase entire blocks |
Can erase/write at byte or sector level |
Density |
Higher storage in smaller size |
Lower density |
Endurance |
Lower endurance (esp. TLC/QLC); needs wear levelling |
Higher endurance in read-heavy, write-light use |
Cost per GB |
Lower |
Higher |
Common Uses |
SSDs, USB drives, SD cards, mobile storage |
Firmware, embedded systems, IoT devices |
Scalability |
Scales with 3D NAND and stacking layers |
Limited scalability |
Power Consumption |
Typically lower |
Slightly higher when active |
Key Applications of NAND Flash Memory
NAND flash shows up in almost every tech product. Here’s where it’s most commonly used:
- Smartphones and Tablets: Stores the OS, apps, and user data. It boots fast and handles heavy read/write activity daily.
- Solid-State Drives (SSDs): Replaces traditional HDDs in laptops and desktops. Massive speed boost with no moving parts.
- USB Flash Drives: Portable storage with plug-and-play access.
- Memory Cards (SD, microSD): Used in cameras, drones, and mobile devices.
- Gaming Consoles: Stores games, updates, and media with minimal loading times.
- Smart TVs and Set-Top Boxes: Load apps, cache content, and store settings.
- Automotive Systems: Powers infotainment systems, cameras, and firmware in modern vehicles.
What's Next for NAND Flash?
NAND flash isn’t standing still. It’s evolving quickly. Here are a few directions:
- More Layers: Manufacturers are moving from 64-layer to 128-layer and beyond in 3D NAND. That means more storage in the same size without sacrificing performance.
- Faster Interfaces: PCIe 5.0 and NVMe 2.0 are making SSDs even faster. Loading times are shrinking, and multitasking feels smoother.
- Better Durability: Newer materials and controller logic are helping TLC and QLC last longer and become more reliable for everyday users.
- AI and Edge Devices: NAND is becoming essential in devices that process data locally, like smart cameras or edge servers. These need fast, durable storage, which NAND delivers.
- Lower Costs: As technology matures, prices keep dropping. That opens the door for NAND to replace spinning drives in even more places.
Wrapping Up
NAND flash memory changed how we store and use data. It’s fast, compact, and built for modern digital life. From phones to servers, it’s the reason our devices boot fast, save quickly, and feel snappy.
If you’re upgrading your storage or building a new setup, it’s worth paying attention to the type of NAND inside—SLC, MLC, TLC, or QLC. Each has its place. And if you’re shopping for memory cards, SSDs, or USB drives, I recommend checking out HugDIY.com. It’s a solid source for memory storage that fits every type of user—from everyday backup to high-speed workflows.